SQUIGGLES Computer Login: Difference between revisions
| (28 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Squiggles is general purpose analysis and storage computer for MEG/Neurophysiology/Epilepsy data | Squiggles server is a general-purpose analysis and storage computer for MEG/Neurophysiology/Epilepsy data | ||
Configuration: | Configuration: | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
For Mac/Linux | For Mac/Linux | ||
==FastX Connection ( | ==FastX Connection (Preferred Connection):== | ||
FastX is an alternative to VNC | FastX is an alternative to VNC connect. It provides a more straightforward connection than VNC. Previously, we have had an issue with a large number of users logging in at once using the VNC. FastX resolves this issue. | ||
The FastX server is installed on squiggles. | The FastX server is installed on squiggles. You will need to download the client - https://www.starnet.com/fastx/current-client | ||
[[File: | [[File: FastX_config.png]] | ||
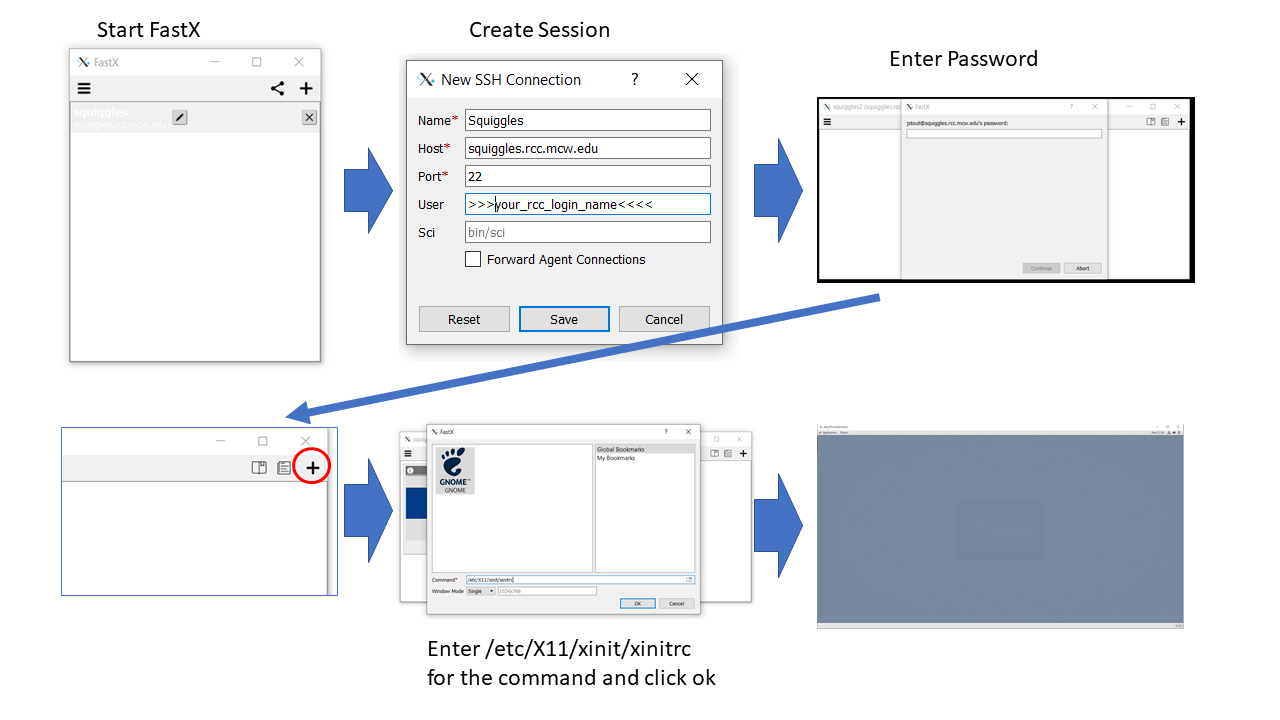
Steps to setup the connection: <br /> | |||
1 | 1. Open fastX <br /> | ||
2 | 2. Click the plus to start a new connection <br /> | ||
3 | 3. Enter the Connection Name, host (sguiggles.rcc.mcw.edu), and user (rcc username) <br /> | ||
4 | 4. Click the plus to enter a session. Use /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc for the command <br /> | ||
==VNC User Ports:== | ==VNC (Old method - still works, FastX may be more reliable)== | ||
===VNC User Ports:=== | |||
(make sure to log in under your port number) | (make sure to log in under your port number) | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
|Vahab Youssofzadeh | |Vahab Youssofzadeh | ||
|5931 | |5931 | ||
|- | |||
|Songhee Kim | |||
|5935 | |||
|} | |} | ||
==Connecting to Squiggles== | ===Connecting to Squiggles=== | ||
===For Mac or Linux=== | ====For Mac or Linux==== | ||
From a bash shell / terminal type the following. This will open a tunnel over ssh to log into VNC Viewer (see below). | From a bash shell / terminal type the following. This will open a tunnel over ssh to log into VNC Viewer (see below). | ||
ssh -N -L 59**:localhost:59** squiggles.rcc.mcw.edu | ssh -N -L 59**:localhost:59** squiggles.rcc.mcw.edu | ||
===For Windows=== | ====For Windows==== | ||
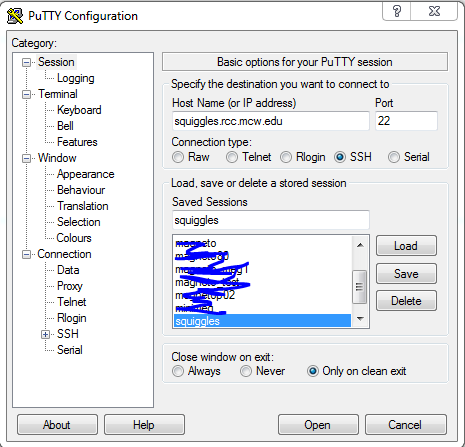
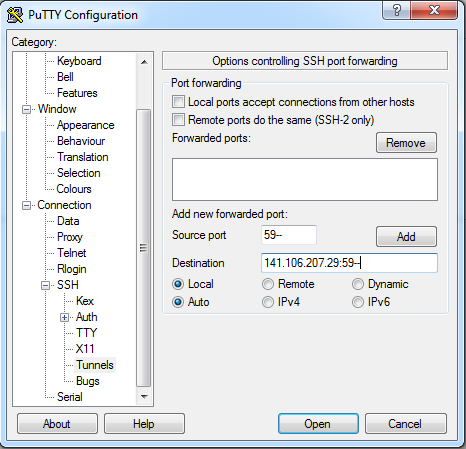
An SSH tunnel must be performed using Putty or with windows 10 you can use the ssh command above. | An SSH tunnel must be performed using Putty or with windows 10 you can use the ssh command above. | ||
| Line 102: | Line 105: | ||
[[File:Putty config2 tunnel.PNG]] | [[File:Putty config2 tunnel.PNG]] | ||
==Logging into VNC session== | ===Logging into VNC session=== | ||
Once connected to squiggles over ssh | Once connected to squiggles over ssh | ||
===Creating a VNC session=== | ====Creating a VNC session==== | ||
VNC sessions will be created at bootup using the port numbers above | VNC sessions will be created at bootup using the port numbers above | ||
If the VNC session fails or is not working: | If the VNC session fails or is not working: | ||
vncserver :## -geometry 1900x1200 | <code>vncserver :## -geometry 1900x1200</code> (This will open a VNC session on port 59## with a resolution of 1900x1200). The ## must match your port number for this to work. | ||
===Connecting to a VNC session=== | |||
====Connecting to a VNC session==== | |||
Use realvnc viewer to log into your VNC session. | Use realvnc viewer to log into your VNC session. | ||
====VNC viewer download==== | =====VNC viewer download===== | ||
Realvnc has been tested to work - https://www.realvnc.com/en/connect/download/viewer/ | Realvnc has been tested to work - https://www.realvnc.com/en/connect/download/viewer/ | ||
====Log in using RealVNC==== | =====Log in using RealVNC===== | ||
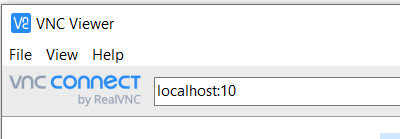
Open vncviewer | Open vncviewer | ||
In the top bar that accepts a VNC Server address < | In the top bar that accepts a VNC Server address and type <code>localhost:##</code> (where ## are the last two digits of your port number 59##) | ||
[[image:vncviewer.png]] | [[image:vncviewer.png]] | ||
Log into the VNC session using your VNC password | Log into the VNC session using your VNC password. Once the VNC window is open, log into the server using your RCC password. <br /> | ||
Once the VNC window is open, log into the server using your RCC password | To reset the password, from the terminal try, <code>vncpasswd</code>. | ||
=====Killing a VNC session===== | |||
From the terminal try, <code>vncserver -kill :xx</code>. Alternatively, for a manual killing, try, <code>rm -f /tmp/.Xxx-lock</code> and <code> rm -f /tmp/.X11-unix/Xxx</code>, followed by <code>vncserver -kill :xx</code> | |||
=====Important Files===== | |||
* <code>bashrc</code> is located at <code>/etc/bashrc</code>(<code>/etc/bash.bashrc</code>) containing system wide functions and aliases. | |||
Latest revision as of 19:10, 11 November 2022
Squiggles server is a general-purpose analysis and storage computer for MEG/Neurophysiology/Epilepsy data
Configuration: For Windows For Mac/Linux
FastX Connection (Preferred Connection):
FastX is an alternative to VNC connect. It provides a more straightforward connection than VNC. Previously, we have had an issue with a large number of users logging in at once using the VNC. FastX resolves this issue.
The FastX server is installed on squiggles. You will need to download the client - https://www.starnet.com/fastx/current-client
Steps to setup the connection:
1. Open fastX
2. Click the plus to start a new connection
3. Enter the Connection Name, host (sguiggles.rcc.mcw.edu), and user (rcc username)
4. Click the plus to enter a session. Use /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc for the command
VNC (Old method - still works, FastX may be more reliable)
VNC User Ports:
(make sure to log in under your port number)
| User | Port |
|---|---|
| Jeff Stout | 5910,5911 |
| Joe Heffernan | 5912 |
| Candida Ustine | 5914 |
| Manoj Raghavan | 5913 |
| Chad Carlson | 5915 |
| Chris Anderson | 5916 |
| Serena Thompson | 5917 |
| Patrick Bauer | 5918 |
| Jeff Binder | 5919 |
| Leo Fernandino | 5920 |
| Lisa Conant | 5921 |
| Lindsay Nelson | 5922 |
| Nick Guzowski | 5923 |
| Zack Harper | 5924 |
| Bill Gross | 5925 |
| Michelle Kassel | 5926 |
| Greg McQuestion | 5927 |
| Monica Keith | 5928 |
| Priyanka Shah | 5929 |
| Vahab Youssofzadeh | 5931 |
| Songhee Kim | 5935 |
Connecting to Squiggles
For Mac or Linux
From a bash shell / terminal type the following. This will open a tunnel over ssh to log into VNC Viewer (see below). ssh -N -L 59**:localhost:59** squiggles.rcc.mcw.edu
For Windows
An SSH tunnel must be performed using Putty or with windows 10 you can use the ssh command above.
Download Putty: https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/
Logging into VNC session
Once connected to squiggles over ssh
Creating a VNC session
VNC sessions will be created at bootup using the port numbers above
If the VNC session fails or is not working:
vncserver :## -geometry 1900x1200 (This will open a VNC session on port 59## with a resolution of 1900x1200). The ## must match your port number for this to work.
Connecting to a VNC session
Use realvnc viewer to log into your VNC session.
VNC viewer download
Realvnc has been tested to work - https://www.realvnc.com/en/connect/download/viewer/
Log in using RealVNC
Open vncviewer
In the top bar that accepts a VNC Server address and type localhost:## (where ## are the last two digits of your port number 59##)
Log into the VNC session using your VNC password. Once the VNC window is open, log into the server using your RCC password.
To reset the password, from the terminal try, vncpasswd.
Killing a VNC session
From the terminal try, vncserver -kill :xx. Alternatively, for a manual killing, try, rm -f /tmp/.Xxx-lock and rm -f /tmp/.X11-unix/Xxx, followed by vncserver -kill :xx
Important Files
bashrcis located at/etc/bashrc(/etc/bash.bashrc) containing system wide functions and aliases.