Squiggles research computer server: Difference between revisions
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
From the terminal try, <br /> | From the terminal try, <br /> | ||
<code>ls -l /tmp/.X11-unix</code> | <code>ls -l /tmp/.X11-unix</code> | ||
Revision as of 17:10, 30 August 2023
Introduction
"Squiggles" is a dedicated research computer server for the analysis and storage of MEG, Neurophysiology, and Epilepsy data. Users can connect to it using either the FastX connection (recommended) or the older VNC method. This guide provides detailed steps for both methods.
Access Requirements
RCC account
To access "Squiggles", users must first have an RCC (Research Computer Server) account.
- Request an account at [MCW-Infoscope's Research Computing Center].
- If asked, select "others" and then "squiggles" to specify the desired server.
- Follow the provided steps to initiate a new session and gain remote access to Squiggles.
How to Access Squiggles
SSH Tunneling Method (for Mac/Linux/Windows)
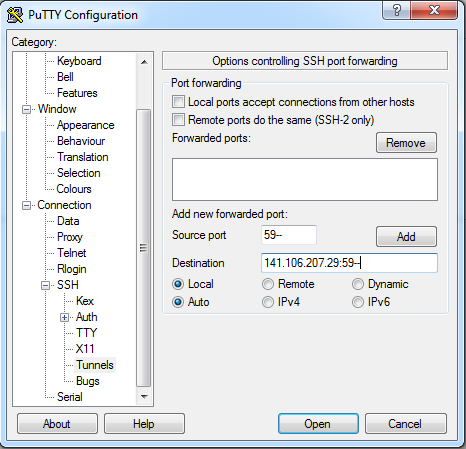
Use the following command in a bash shell, terminal or Windows power shell to establish an SSH tunnel for the VNC Viewer:
ssh -N -L 59**:localhost:59** squiggles.rcc.mcw.edu
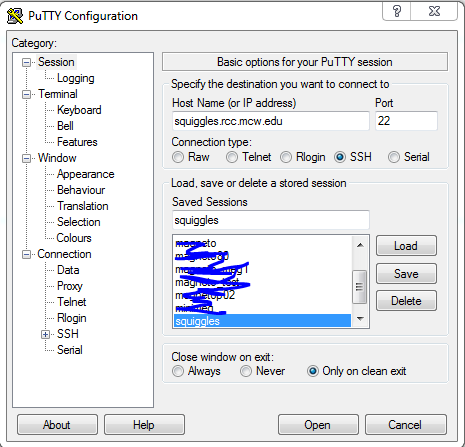
VNC Method (for Windows)
Configuration:
- Download Putty.
VNC User Ports:
Users must log in using their designated port numbers. Below is the list of users and their respective ports:
| User | Port |
|---|---|
| Jeff Stout | 5910,5911 |
| Joe Heffernan | 5912 |
| Candida Ustine | 5914 |
| Manoj Raghavan | 5913 |
| Chad Carlson | 5915 |
| Chris Anderson | 5916 |
| Serena Thompson | 5917 |
| Patrick Bauer | 5918 |
| Jeff Binder | 5919 |
| Leo Fernandino | 5920 |
| Lisa Conant | 5921 |
| Aqil Izadysadr | 5922 |
| Nick Guzowski | 5923 |
| Zack Harper | 5924 |
| Bill Gross | 5925 |
| Michelle Kassel | 5926 |
| Greg McQuestion | 5927 |
| Monica Keith | 5928 |
| Priyanka Shah | 5929 |
| Vahab Youssofzadeh | 5931 |
| Songhee Kim | 5935 |
| Cameron J Stewart | 5992 |
Creating a VNC Session
- VNC sessions auto-start at bootup using the above-listed port numbers.
- If you encounter any issues, initiate a session manually using:
vncserver :## -geometry 1900x1200. Replace##with your specific port number.
Connecting to a VNC Session
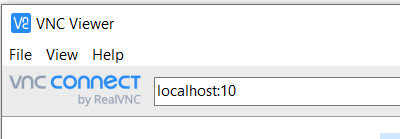
RealVNC method:
- To access, use the [RealVNC viewer].
- In the server address bar, input
localhost:##, where##corresponds to the last two digits of your port number. - Authenticate using both your VNC and RCC credentials.
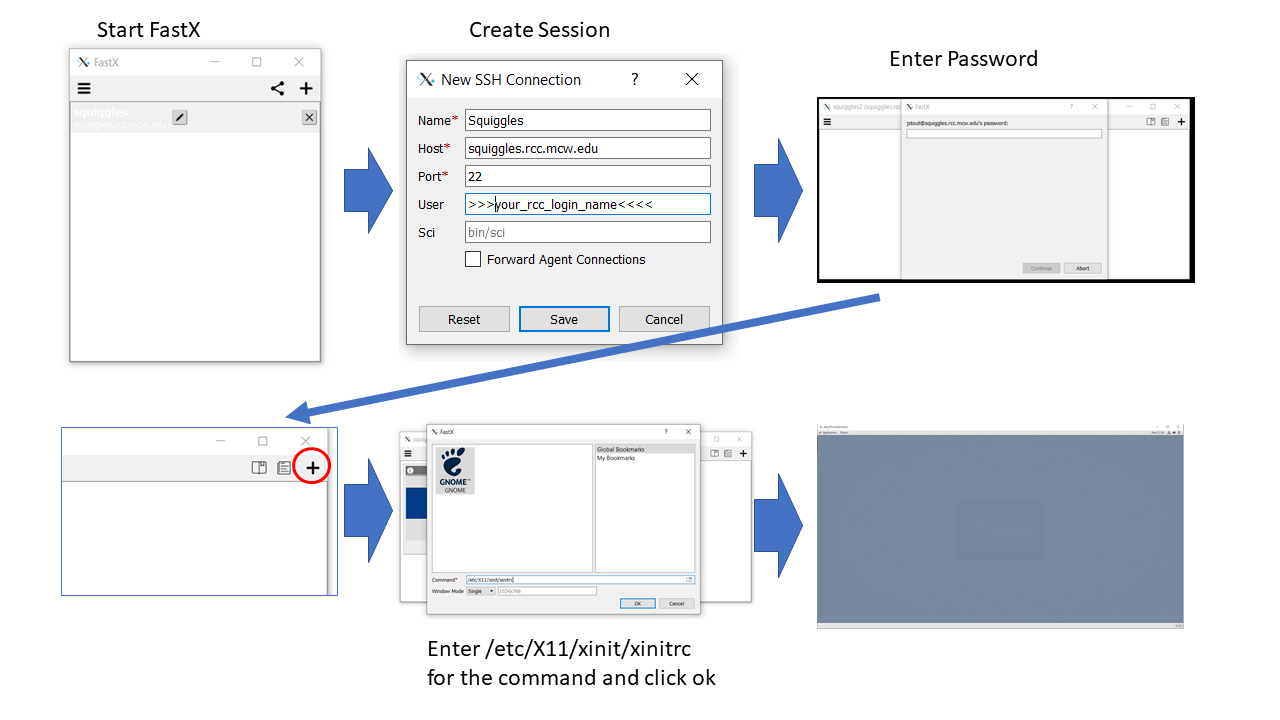
FastX Method:
- FastX may offer a more user-friendly connection than VNC and address issues related to a large number of simultaneous VNC users.
- Download the FastX client and follow these steps:
- Open FastX.
- Click the '+' to initiate a new connection.
- Provide the Connection Name, host (squiggles.rcc.mcw.edu), and user (your RCC username).
- To enter a session, click the '+' and use /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc as the command.
Troubleshooting
Common issues & Solutions
- VNC Black Screen: If VNC shows a black screen after login, ensure Anaconda Python is deactivated before creating the VNC session. Use the
conda deactivatecommand in the terminal. - FastX as an Alternative: If you experience persistent issues with VNC, consider using the FastX method described above.
Additional VNC Session Management:
- Killing a VNC session: In the terminal, use
vncserver -kill :xx/. If required to kill manually, execute:
rm -f /tmp/.Xxx-lock rm -f /tmp/.X11-unix/Xxx
- List of Active Users: Use the command
ls -l /tmp/.X11-unixin the terminal.
List of users
From the terminal try,
ls -l /tmp/.X11-unix