Squiggles research computer server
Introduction
"Squiggles" is a research computer server dedicated to the analysis and storage of MEG/Neurophysiology/Epilepsy data. This page provides a comprehensive guide on how to access and utilize the server. There are two primary methods to connect: the preferred FastX connection and the older VNC method.
How to Access Squiggles
Squiggles server is general purpose analysis and storage computer for MEG/Neurophysiology/Epilepsy data
Configuration: For Windows For Mac/Linux
RCC account
To access the "Squiggles" server, an RCC (research computer server) account is required. Submit requests to MCW-Infoscope (https://infoscope.mcw.edu/RCC/Research-Computing-Center.htm). If prompted, select "others" and "squiggles" to specify the desired server. Follow the subsequent steps to initiate a new session, log in (using Putty or SSH tunneling), and remotely access Squiggles via VNC Viewer (https://www.realvnc.com/en/connect/download/viewer/).
FastX Connection (alternative connection)
FastX is an alternative to VNC connect. It provides a more straightforward connection than VNC. Previously, we had an issue with a large number of users logging in at once using the VNC. FastX resolves this issue.
The FastX server is installed on squiggles. You will need to download the client - https://www.starnet.com/fastx/current-client
Steps to setup the connection:
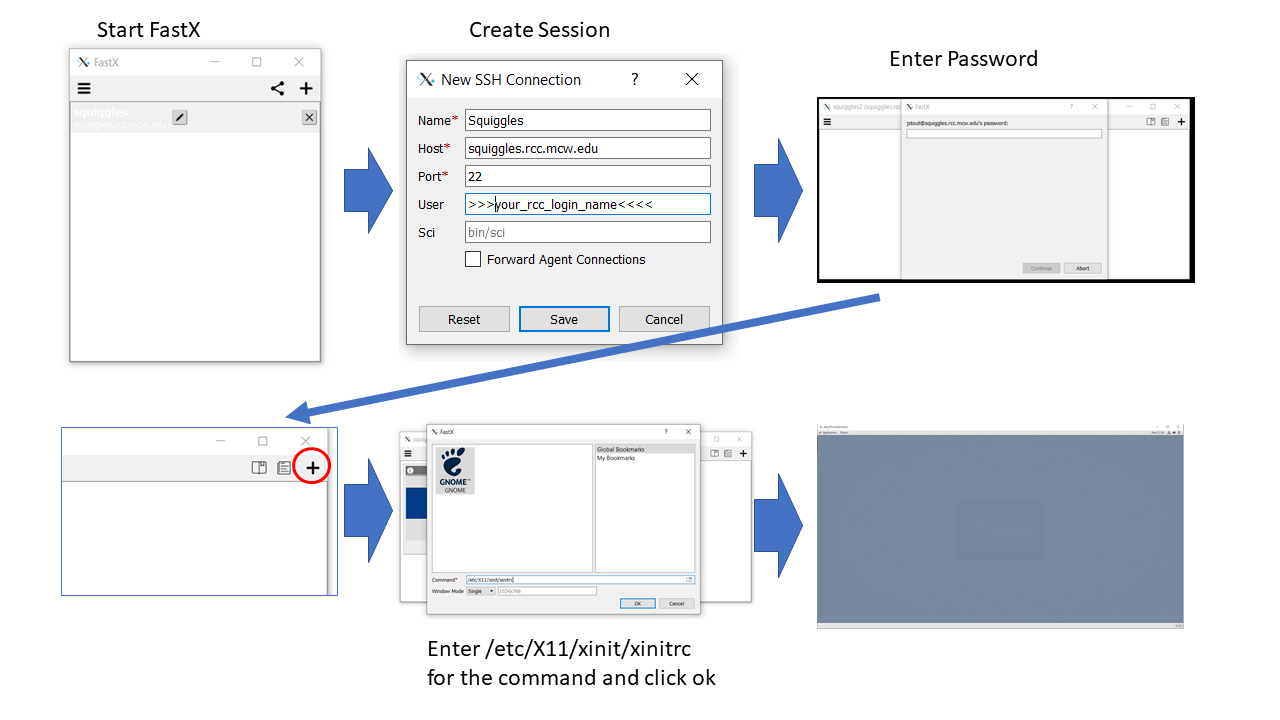
1. Open fastX
2. Click the plus to start a new connection
3. Enter the Connection Name, host (squiggles.rcc.mcw.edu), and user (rcc username)
4. Click the plus to enter a session. Use /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc for the command
VNC (Old method - still works, FastX may be the alternative)
VNC User Ports:
(Make sure to log in under your port number)
| User | Port |
|---|---|
| Jeff Stout | 5910,5911 |
| Joe Heffernan | 5912 |
| Candida Ustine | 5914 |
| Manoj Raghavan | 5913 |
| Chad Carlson | 5915 |
| Chris Anderson | 5916 |
| Serena Thompson | 5917 |
| Patrick Bauer | 5918 |
| Jeff Binder | 5919 |
| Leo Fernandino | 5920 |
| Lisa Conant | 5921 |
| Aqil Izadysadr | 5922 |
| Nick Guzowski | 5923 |
| Zack Harper | 5924 |
| Bill Gross | 5925 |
| Michelle Kassel | 5926 |
| Greg McQuestion | 5927 |
| Monica Keith | 5928 |
| Priyanka Shah | 5929 |
| Vahab Youssofzadeh | 5931 |
| Songhee Kim | 5935 |
| Cameron J Stewart | 5992 |
Connecting to Squiggles
For Mac or Linux
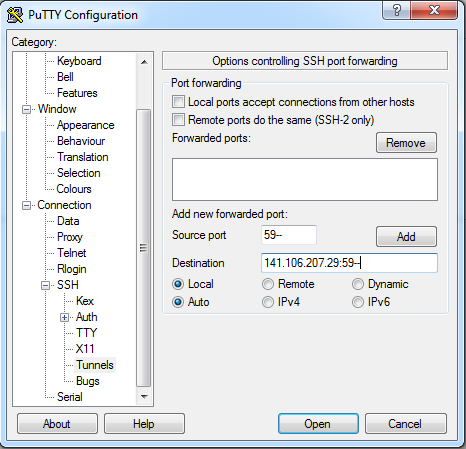
From a bash shell / terminal type the following. This will open a tunnel over ssh to log into VNC Viewer (see below).
/ssh -N -L 59**:localhost:59** squiggles.rcc.mcw.edu
For Windows
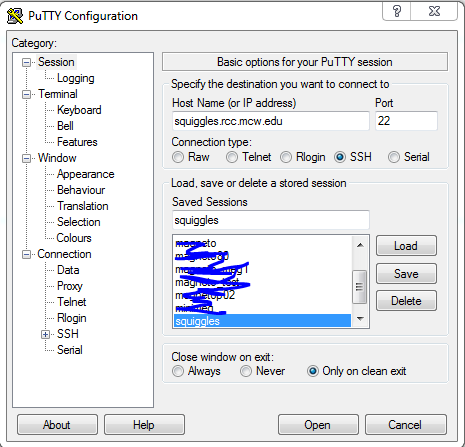
An SSH tunnel must be performed using Putty or with windows 10 you can use the ssh command above.
Download Putty: https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/
Logging into VNC session
Once connected to squiggles over ssh
Creating a VNC session
VNC sessions will be created at bootup using the port numbers above
If the VNC session fails or is not working:
vncserver :## -geometry 1900x1200 (This will open a vnc session on port 59## with a resolution of 1900x1200) The ## must match your port number for this to work.
Connecting to a VNC session
Use realvnc viewer to log into your VNC session.
VNC viewer download
Realvnc has been tested to work - https://www.realvnc.com/en/connect/download/viewer/
Log in using RealVNC
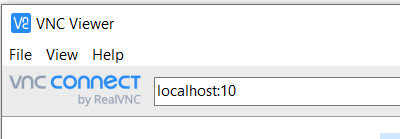
Open vncviewer
In the top bar that accepts a VNC Server address
type localhost:## (where ## are the last two digits of your port number 59##)
Log into the VNC session using your VNC password
Once the VNC window is open, log into the server using your RCC password
Killing a VNC session
From the terminal try,
vncserver -kill :xx
for a manual kill (if asked) try,
rm -f /tmp/.Xxx-lock rm -f /tmp/.X11-unix/Xxx
List of users
From the terminal try,
ls -l /tmp/.X11-unix
Common issues & Solutions
- Before a VNC session is created, anaconda python must be deactivated. Enter
conda deactivateinto the terminal. If the user does not deactivate anaconda python, VNC will start, but a black screen is shown after logging in.